Why Choose Barefoot For Your Horse?
Why Choose Barefoot For Your Horse?
The horse’s hooves have been designed by nature to function optimally when barefoot. Properly trimmed barefoot hooves allow the hoof to flex, which facilitates circulation in and out of the feet. This process is assisted by continuous movement by the horse. The horse depends on this flexing of the hoof for circulation and thus health.
Barefoot enables the horse’s feet to be maintained in a physiologically correct framework, so they are able to move correctly and rest comfortably and can ultimately remain functional at all times. It provides the opportunity to develop strong and healthy foundations beneath a horse, which leads to better long term soundness.
What Are Some Other Benefits of Barefoot?
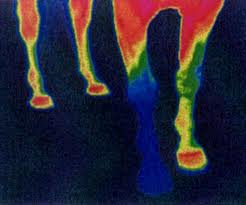
Thermographic image shows the shod leg (right front) to have a lower temperature than the three barefoot legs.
In addition to improving the horse’s overall health, the improved blood flow encourages the hoof to grow, enabling it to keep up with wear. The hoof horn is also stronger and healthier.
Because the temperature of the legs is higher than those of shod horses, the metabolism functions more efficiently, enabling the horse to fight pathogens (such as rainrot and infections)
The ‘reversible deformation’ of the flexing hoof provides greater shock absorption. This leads to fewer injuries and less wear and tear to the horse’s body and increased useful life span.
The lack of heavy iron on the limb results in fewer injuries to themselves, other horses, as well as humans. The bare hoof has better traction on all types of terrain. Finally, the barefoot horse’s proprioception functions correctly and the horse travels more sure-footedly.
What is Proper Physiological Hoof Trimming?
Physiological trimming recognizes physiological features of the whole horse and promotes proper functioning. It aims to achieve whole-horse soundness.
There is more to barefoot than removing the shoes!
- Treat the cause, not the symptom
- Establish correct form
It is not just simply a case of removing the shoes and applying a conventional trim. The first step is to apply a physiologically correct trim which includes the following:
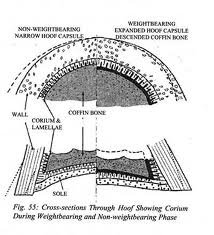
A tight laminar connection resulting from the elimination of flares which ensures that the coffin bone is well suspended in the hoof capsule. The walls are trimmed so that the sole is also weight bearing (avoiding peripheral loading). It ensures that the bottom edge of the coffin bone is near-parallel to the ground which promotes hoof mechanism and thus circulation, and maintains correct loading on the joints, which prevents boney irregularities and joint problems. 
The first step is to return the feet to the correct parameters and keep them within a functional framework. This facilitates correct movement and resting posture. A functional foot is mostly related to the following parameters:
. The landing gear (back half of the frog and heel platforms) is well developed.
. Weight bearing surface consists of the inner wall, some sole and the majority of frog.
. Outer wall and quarters and bars remain “passive” when standing on hard surfaces.
. Three dimensional balance is dictated by sole plane.
. Functional sole plane is left intact to protect internal structures.
. Functional frog is left intact to protect internal structures.
. Breakover balance is short with a third or less of weight bearing foot surface in front of the point of frog.